What Are the Oral Cancer Stages?
What Is Oral Cancer?
This particular kind of cancer is usually found in mouth and throat tissue and it can form anywhere in the surrounding area. Oral cancer of a larger group of cancers, commonly known as head and neck cancers and it will normally develop in the cells found in your mouth, tongue, or lips. Detection at an early stage is the key to surviving this potentially fatal disease before it begins having a serious impact on your lifestyle and overall health.
The Different Types of Oral Cancers
Oral cancer is the umbrella term given to a range of different cancers including cancers of the following areas:
- Lips
- Tongue
- Cheeks
- Gums
- Palate (hard and soft)
- The mouth floor
The first healthcare provider to observe symptoms of oral cancer is usually your dentist.
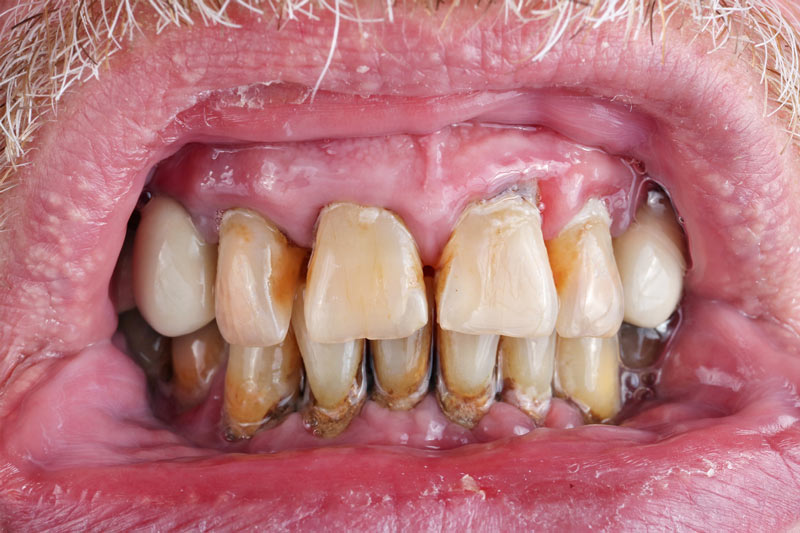
Symptoms
Here are just a few of the symptoms of oral cancer. If you find you are experiencing any of the following, contact your dentist for a checkup:
- If you notice a growth in your mouth or throat
- Sores on your lips or mouth that won’t heal
- Teeth that are loose
- Your mouth is bleeding
- You have difficulty wearing dentures
- Swallowing is painful
- A lump on your neck
- Numbness in the face, neck, lip or chin
- Extreme weight loss
- A painful tongue
- Your jaw is painful or still
- A continuous sore throat
The Different Stages of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is typically categorized into four stages. During the first two stages, you will likely have developed a small tumor. The final stages—stages 3 and 4—are the stages you need to worry about as, by then, the cancer is advanced. One of the main reasons that it is crucial to get an early diagnosis is that, during the first two stages, it is unlikely that the cancerous cells will manage to spread to your lymph nodes. This typically occurs during stages 3 and 4 once the tumors have grown larger and cancer has the power to spread to your lymph nodes, as well as other parts of the body. The yearly survival rate of patients who suffer from oral cancer is 81% after the first year, 56% after 5 years, and, after 10 years, the survival rate is just 41%. Therefore, if you are lucky enough to diagnose the problem early on, your post-treatment survival chances will be much higher.
What Are the Causes of Oral Cancer?
How Is Oral Cancer Treated?
Treatment for oral cancer will vary depending on the area and stage of your cancer on receiving your diagnosis. Early stage cancer treatment usually involves surgery to remove the tumor and cancerous lymph nodes. If your physician feels it is necessary, tissues surrounding the mouth and neck may also be removed to prevent the cancer from returning or spreading. Aside from surgery, there are also other options that are commonly used to treat oral cancer, such as the following:
Radiation Therapy. During radiotherapy, radiation beams are fired at the tumor a couple of times a day, 5 days a week. If oral cancer is in its final stages, then radiation therapy is usually used alongside chemo.
Chemotherapy. Perhaps the most aggressive and well-known cancer treatment, chemotherapy works to kill cancerous cells using drugs. The medicine is administered via an intravenous tube and is performed on an outpatient basis.
Changes to Your Diet. Many people underestimate the importance of maintaining a healthy, balanced diet. It is especially important with regards to treating oral cancer, as many patients struggle to eat properly due to the pain in their mouth. This, in turn, leads to dramatic weight loss and a poor appetite. A nutritionist will be able to create a healthy diet plan for you that will be easy on the mouth, but still contain all of the essential nutrients that your body needs to regain strength.
Can Visiting the Dentist Help Treat Oral Cancer?
While a dentist will only be able to diagnose (not treat) oral cancer, visiting a dentist for frequent check-ups is going to be your best option with regards to preventing oral cancer. If you have a good dental hygiene routine, your chances of developing oral cancer are slimmer. And, if you do fall victim to this potentially fatal disease, your dentist will be able to diagnose it before it advances into its final stages and refer you a physician to discuss your treatment options.
Relate Posts to Read:
Oral Cancer Survival Rate by Age
